|
Min Woo Sun I’m a PhD candidate at Stanford developing machine learning methods to advance biomedical research and clinical care. My work focuses on training biomedical vision-language models and building large-scale open-source datasets to create reproducible, generalizable, and clinically meaningful AI for applications in areas like precision oncology. I'm fortunate to be jointly advised by Serena Yeung-Levy and Robert Tibshirani, and to be supported by the National Library of Medicine T15 grant, ARPA-H, and the Stanford Data Science Scholars fellowship. In March 2026, I will join Google DeepMind as a PhD Student Researcher. Most recently, I was a Machine Learning Engineer intern at Hugging Face. Previously, I worked on NGS lab workflows at Invitae and early cancer detection at Guardant Health. |

|
News
|
Selected Publications(*) denotes co-first authorship. For a full list of publications, please check my Google Scholar |
|
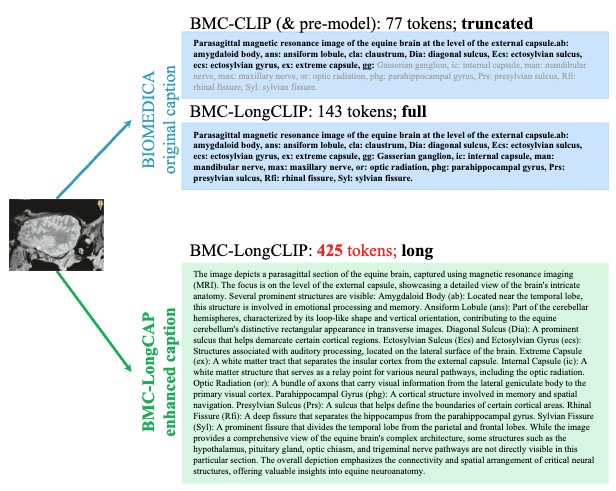
No Tokens Wasted: Leveraging Long Context in Biomedical Vision-Language Models
Min Woo Sun*, Alejandro Lozano*, Javier Gamazo Tejero, Vishwesh Nath, Xiao Xiao Sun, James Burgess, Yuhui Zhang, Kun Yuan, Robert Tibshirani, Sean Huver, Serena Yeung-Levy TBD 2025 Collaboration with NVIDIA arXiv / github / data We introduce BMC-LongCLIP, a biomedical vision-language embedding model with extended text capacity (up to 512 tokens) trained on BIOMEDICA-LongCAP, a dataset of 1M context-rich image–caption pairs. The model reduces token waste from 55 % to 2.2 % and achieves +30 % Recall@1 and faster convergence, highlighting the promise of long-context modeling for biomedical vision-language models. |
|
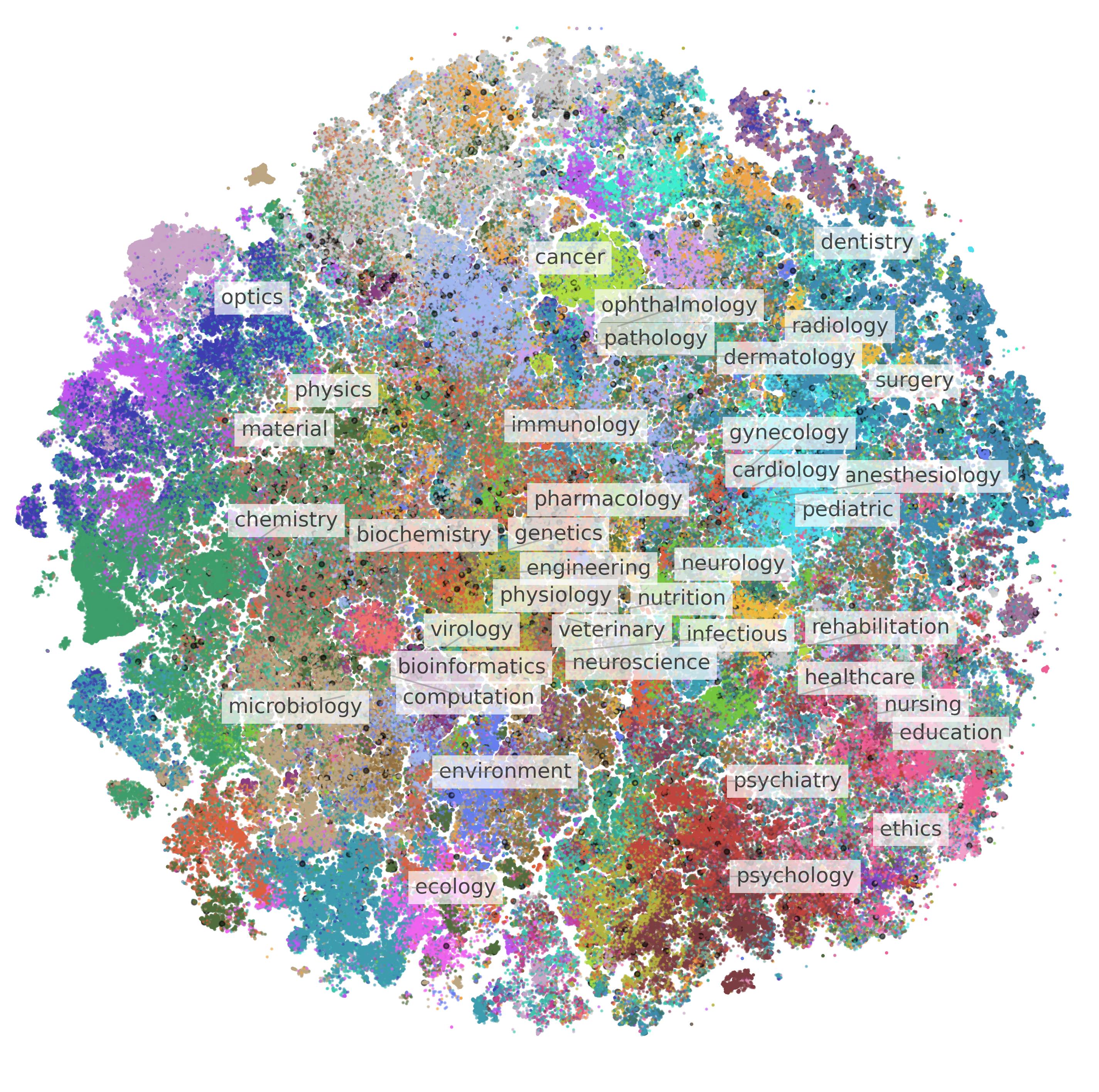
BIOMEDICA: An Open Biomedical Image-Caption Archive, Dataset, and Vision-Language Models Derived from Scientific Literature
Alejandro Lozano*, Min Woo Sun*, James Burgess*, Liangyu Chen, Jeffrey J. Nirschl, Jeffrey Gu, Ivan Lopez, Josiah Aklilu, Anita Rau, Austin Wolfgana Katzer, Yuhui Zhang, Collin Chiu, Xiaohan Wang, Alfred Seunghoon Song, Robert Tibshirani, Serena Yeung-Levy CVPR 2025 arXiv / github / data / project page We introduce BIOMEDICA, an open-source framework that transforms the PubMed Central Open Access subset into a comprehensive dataset of over 24 million image-text pairs with expert-guided annotations, enabling state-of-the-art performance in biomedical vision-language models across diverse tasks and domains. |
|
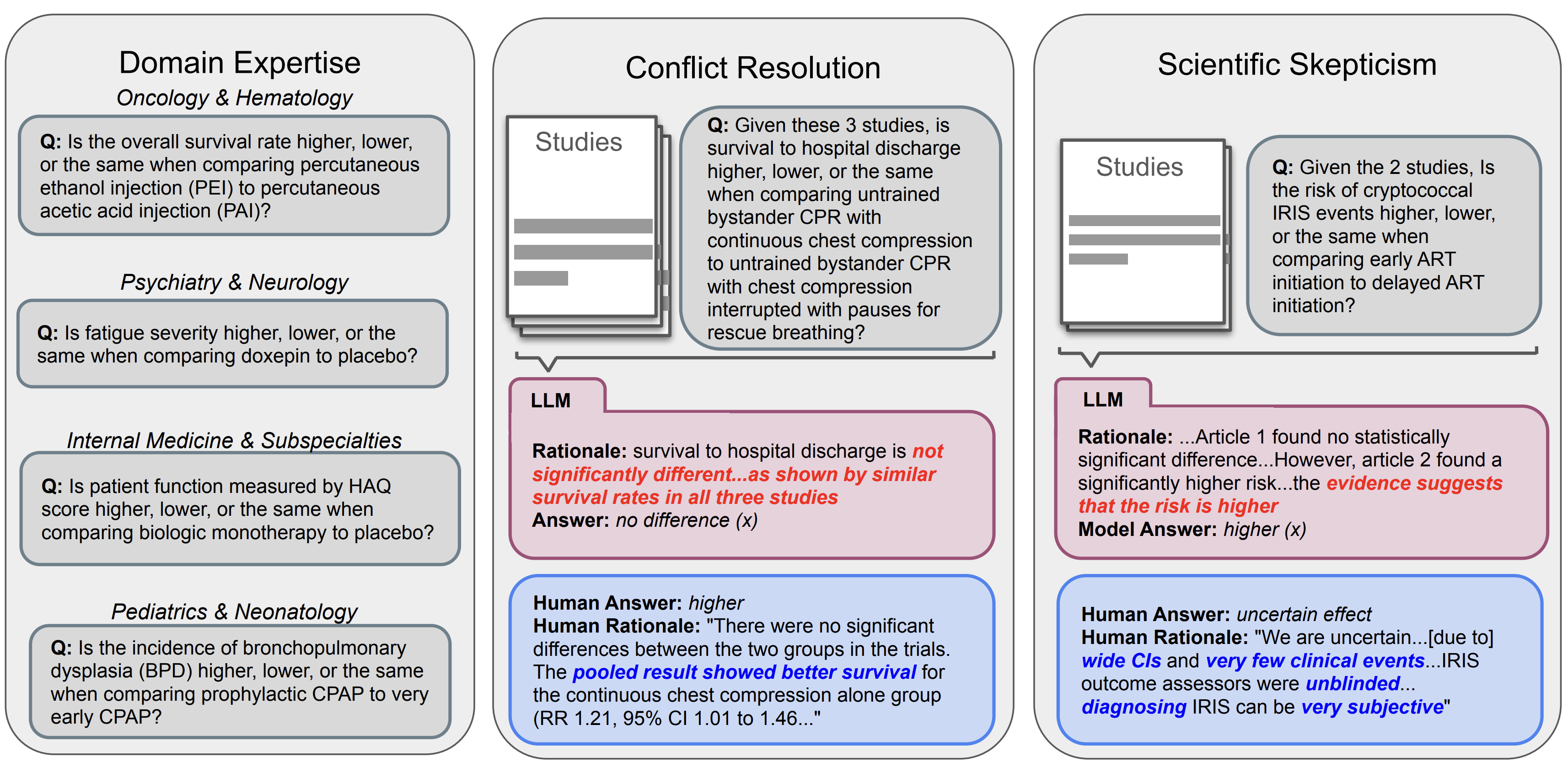
Can Large Language Models Match the Conclusions of Systematic Reviews?
Christos Polzak*, Alejandro Lozano*, Min Woo Sun*, James Burgess, Yuhui Zhang, Kevin Wu, Serena Yeung-Levy TBD, 2025 project page / github / Data Can LLMs match the conclusions of systematic reviews written by clinical experts when given access to the same studies? To explore this question, we present MedEvidence, A human-curated benchmark of 284 questions (from 100 open-access SRs) across 10 medical specialties. |
|
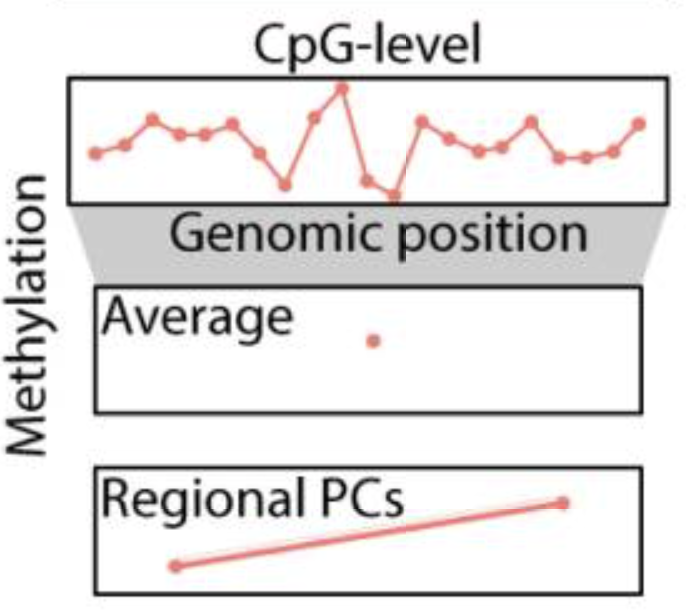
regionalpcs: improved discovery of DNA methylation associations with complex traits
Tiffany Eulalio, Min Woo Sun, Olivier Gevaert, Michael D. Greicius, Thomas J. Montine, Daniel Nachun, Stephen B. Montgomery Nature Communications, 2025 (featured in Nature Comm Editor's Highlight) Nature Communications / github / Bioconductor Functions to summarize DNA methylation data using regional principal components. Regional principal components are computed using principal components analysis within genomic regions to summarize the variability in methylation levels across CpGs. |
|
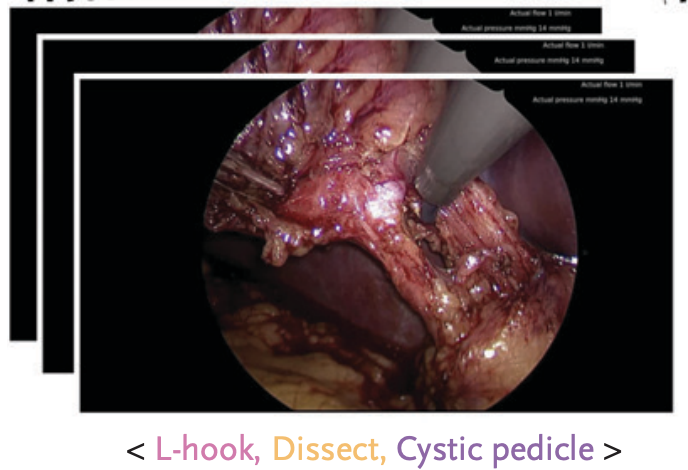
Artificial Intelligence Identifies Factors Associated with Blood Loss and Surgical Experience in Cholecystectomy
Josiah G. Aklilu, Min Woo Sun, Shelly Goel, Sebastiano Bartoletti, Anita Rau, Griffin Olsen, Kay S. Hung, Sophie L. Mintz, Vicki Luong, Arnold Milstein, Mark J. Ott, Robert Tibshirani, Jeffrey K. Jopling, Eric C. Sorenson, Dan E. Azagury, Serena Yeung-Levy NEJM AI, 2024 NEJM AI / github We developed a computer vision model to analyze laparoscopic surgery videos, identifying fine-grained surgical actions linked to operative blood loss and surgeon experience. |
|
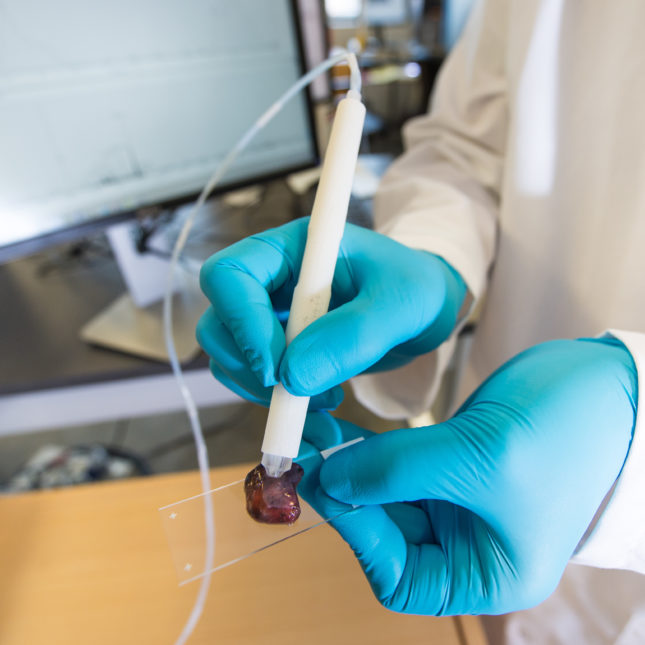
Intraoperative Evaluation of Breast Tissues During Breast Cancer Operations Using the MasSpec Pen
Kyana Y. Garza, Mary E. King, Chandandeep Nagi, Rachel J. DeHoog, Jialing Zhang, Marta Sans, Anna Krieger, Clara L. Feider, Alena V. Bensussan, Michael F. Keating, John Q. Lin, Min Woo Sun, Robert Tibshirani, Christopher Pirko, Kirtan A. Brahmbhatt, Ahmed R. Al-Fartosi, Alastair M. Thompson, Elizabeth Bonefas, James Suliburk, Stacey A. Carter, Livia S. Eberlin JAMA Network, 2024 JAMA Network Molecular data from mass spectrometry were used to build classifiers, achieving high diagnostic accuracy when compared to pathology results, highlighting its potential for real-time surgical guidance. |
|
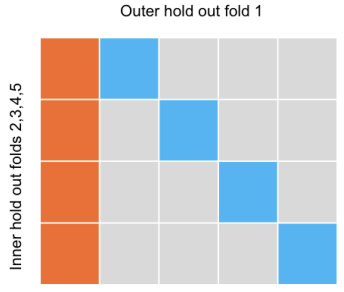
Confidence intervals for the Cox model test error from cross-validation
Min Woo Sun, Robert Tibshirani Statistics in Medicine, 2023 Statistics in Medicine / arXiv / github Cross-validation (CV) can underestimate test error variance due to correlated error estimates from using the same samples for training and testing. Nested CV mitigates this issue by providing more accurate coverage through improved error variance estimation, which this work extends to the Cox proportional hazards model. |
|
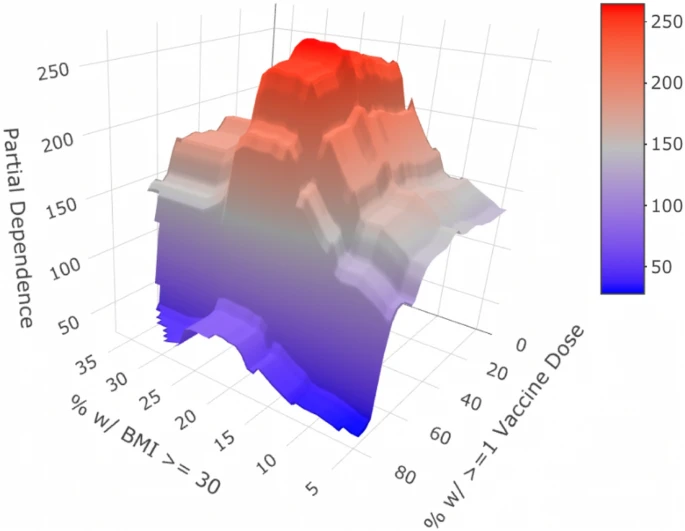
Public health factors help explain cross country heterogeneity in excess death during the COVID19 pandemic
Min Woo Sun*, David Troxell*, Robert Tibshirani Nature Scientific Reports, 2023 Nature Scientific Reports / github The COVID-19 pandemic has caused 14.9 million excess deaths globally, with prior studies linking cross-country differences in COVID-19 deaths to demographic and health factors. This analysis extends the scope by incorporating government policies, showing the critical role of public health efforts in reducing excess deaths. |
|
Game theoretic centrality: a novel approach to prioritize disease candidate genes by combining biological networks with the Shapley value
Min Woo Sun, Stefano Moretti, Kelley M. Paskov, Nate T. Stockham, Maya Varma, Brianna S. Chrisman, Peter Y. Washington, Jae-Yoon Jung, Dennis P. Wall BMC Bioinformatics, 2020 BMC We introduce game theoretic centrality, which integrates biological network knowledge with Shapley value from coalitional game theory to prioritize disease-associated genes. Applied to autism spectrum disorder (ASD), the approach identifies biologically relevant genes, demonstrating potential regulatory interactions and offering insights into the genetic basis of complex disorders. |